“Zinc-Finger Transcription Factor ZAT6 Positively Regulates Cadmium Tolerance through Glutathione-dependent Pathway in Arabidopsis”, the study conducted by the research group of Professor Cao Shuqing from the School of Food Science and Engineering, was published on Plant Physiology (http://www.plantphysiol.org/content/early/2016/03/16/pp.15.01882; Five-Year Impact Factor: 8.030). The study was funded by the Major Project for Genetic Modification and National Nature Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
The heavy metal pollution of soil is one of the major global environmental issues. The heavy metal in the soil can be absorbed by crops and intrude into the food chain, constituting a severe threat to food safety and human health. While Genetic Engineering in the improvement of plants is one of the most important ways to solve this problem, discovering the key gene that is heavy-metal tolerant and heavy metal hyperaccumulating is the key to containing agricultural food safety at its source.
In the study, an Arabidopsis Cd-resistant mutant xcd2-D (XVE system-induced cadmium-tolerance) is identified using a forward genetics approach. The mutant gene underlying xcd2-D mutation was revealed to encode a known zinc-finger transcription factor ZAT6. Transgenic plants overexpressing ZAT6 showed significant increase of Cadmium (Cd) tolerance, whereas loss-of-function of ZAT6 led to decreased Cd tolerance. ZAT6 coordinately activates PC-synthesis related gene expression and directly targets GSH1 to positively regulate Cd accumulation and tolerance in Arabidopsis. (Figure 1)
The study reveals, for the first time in the world, that ZAT6 coordinately activates PC-synthesis related gene expression and directly targets GSH1 to positively regulate Cd accumulation and tolerance in Arabidopsis, thus providing new gene resource and technical channels to genetic Engineering in the improvement of plants. The gene has been granted an independent patent (Patent Number: ZL201310446574.7) for its application in the improvement of Cd polluted soil.
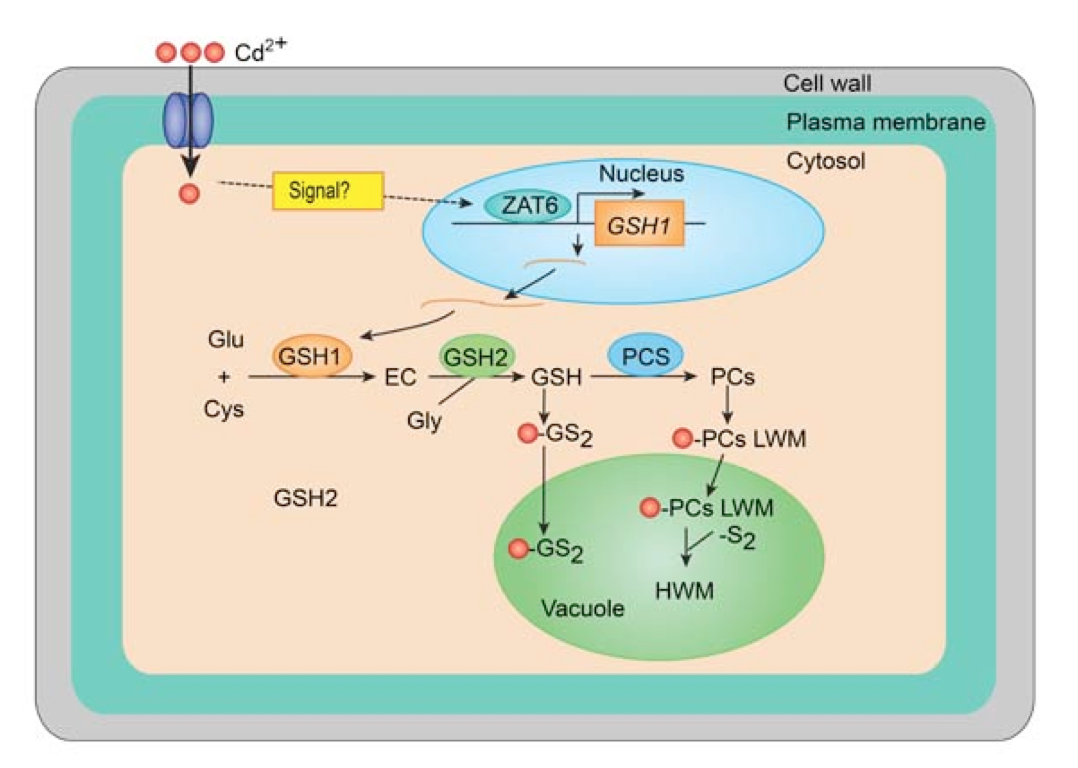
Figure 1. The role of ZAT6 in regulating Cd toleration and tolerance
Written by & photo credit: Zhou Jianyu
Edited by: Wang Jian
编辑:闵旋


 HOME
/
Content
HOME
/
Content
